Reorder matrix rows or columns
Permute Matlab Example
此 MATLAB 函数 按照向量 dimorder 指定的顺序重新排列数组的维度。例如,permute(A,2 1) 交换矩阵 A 的行和列维度。. How to permute binary numbers to a specific. Learn more about permutation. Rearrange the dimensions of a multidimensional array. B = permute(A,order) Description. B = permute(A,order) rearranges the dimensions of A so that they are in the order specified by the vector order. B has the same values of A but the order of the subscripts needed to access any particular element is rearranged as specified.
- Library:
DSP System Toolbox / Math Functions / Matrices and Linear Algebra / Matrix Operations
Description
The Permute Matrix block reorders the rows or columns of an M-by-N input matrix A as specified by indexing input P.
Ports
Input
Input matrix, specified as a scalar, vector, or matrix.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated
Index matrix, specified as a scalar or vector.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | enumerated
Output
Output signal, specified as a vector or matrix.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated
Parameters
Method of constructing the output matrix by permuting rows or columns of the input.
When the Permute parameter is set to:
Rows–– The block uses the rows ofAto create a matrix that has the same column dimension. InputPis a length-L vector whose elements determine where each row fromAmust be placed in the L-by-N output matrix.For row permutation, the block treats the length-M unoriented vector input at the port
Aas an M-by-1 matrix.Columns–– The block uses the columns ofAto create a matrix that has the same row dimension. InputPis a length-L vector whose elements determine where each column fromAmust be placed in the M-by-L output matrix.For column permutation, the block treats the length-N unoriented vector input at port
Aas a 1-by-N matrix.
Index mode — Index mode
Zero-based (default) | One-based
When set to One-based, a value of 1 in the permutation vector P refers to the first row or column of the input matrix A. When set to Zero-based, a value of 0 in P refers to the first row or column of A.
Invalid permutation index — Response to an invalid index value
Clip index (default) | Clip and warn | Generate error
Response to an invalid index value. When an index value in input P references a nonexistent row or column of matrix A, the block reacts as specified in this parameter. These options are available:
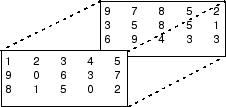
Clip index–– Clip the index to the nearest valid value (1 or M for row permutation and 1 or N for column permutation) and do not issue an alert. Example: For a 3-by-7 input matrix, a column index of 9 is clipped to 7 and a row index of -2 is clipped to 1.Clip and warn–– Display a warning message in the MATLAB® Command Window and clip the index as described in the preceding bullet.Generate error–– Display an error dialog box and terminate the simulation.
Tunable: Yes
Error when length of P is not equal to Permute dimension size — Error message for P length
off (default) | on
Option to display an error dialog box and terminate the simulation when the length of the permutation vector P is not equal to the number of rows or columns of the input matrix A.
You can choose to open an error dialog box and terminate the simulation by setting this parameter to on.
Model Examples
Simulink® model example that shows how to permute a matrix by rows or columns.
The application envisioned for this example is automatic lane tracking on a road. We will show how to fit a polynomial to noisy data representing the lane boundary of the road ahead of a vehicle.
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Generated code relies on memcpy or memset functions (string.h) under certain conditions.
Fixed-Point Conversion
Design and simulate fixed-point systems using Fixed-Point Designer™.
See Also
Blocks
- Submatrix | Variable Selector
Functions
Topics
Rearrange dimensions of multidimensional array dimensions
Description
The Permute Dimensions block reorders the elements of the input signal by permuting its dimensions. You specify the permutation to be applied to the input signal using the Order parameter.
For example, to transpose a 3-by-5 input signal, specify the permutation vector [2 1] for the Order parameter. When you do, the block reorders the elements of the input signal and outputs a 3-by-5 matrix.
You can use an array of buses as an input signal to a Permute Dimensions block. For details about defining and using an array of buses, see Combine Buses into an Array of Buses.
Input
Permute Matlab Random
Port_1 — Input signal
scalar | vector | matrix | N-D array
This port accepts scalar, vector, matrix, and N-dimensional signals of any data type that Simulink® Viscosity 1 8 45. supports, including fixed-point, enumerated, and nonvirtual bus data types.
Data Types: half | single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
Output
Port_2 — Permutation of input signal
scalar | vector | matrix | N-D array
The block outputs the permutation of the input signal, according to the value of the Order parameter. The output has the same data type as the input.
Data Types: half | single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
Parameters
Order — Permutation vector
[2,1] (default) | N-element vector, where N is the number of dimensions of the input signal
Specify the permutation order to apply to the dimensions of the input signal. The value of this parameter must be an N-element vector where N is the number of dimensions of the input signal. The elements of the permutation vector must be a rearrangement of the values from 1 to N.
For example, the permutation vector [2 1] applied to a 5-by-3 input signal results in a 3-by-5 output signal, in other words, the transpose of the input signal.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter: Order |
| Type: character vector |
| Value: N-element vector |
Default: '[2 1]' |
Model Examples
Use the Permute Dimensions block to permute the first and third dimensions of a 3-by-4-by-5 input array.
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
PLC Code Generation
Generate Structured Text code using Simulink® PLC Coder™.
Fixed-Point Conversion
Design and simulate fixed-point systems using Fixed-Point Designer™.
See Also
Math Function | permute
